Fuzzy Search for Your Git Repository
Created: – Last Updated:
In this article, you’ll learn how to use fzf-git (opens in a new tab) to fuzzy search your local git repository.
Here’s what a branch search looks like:
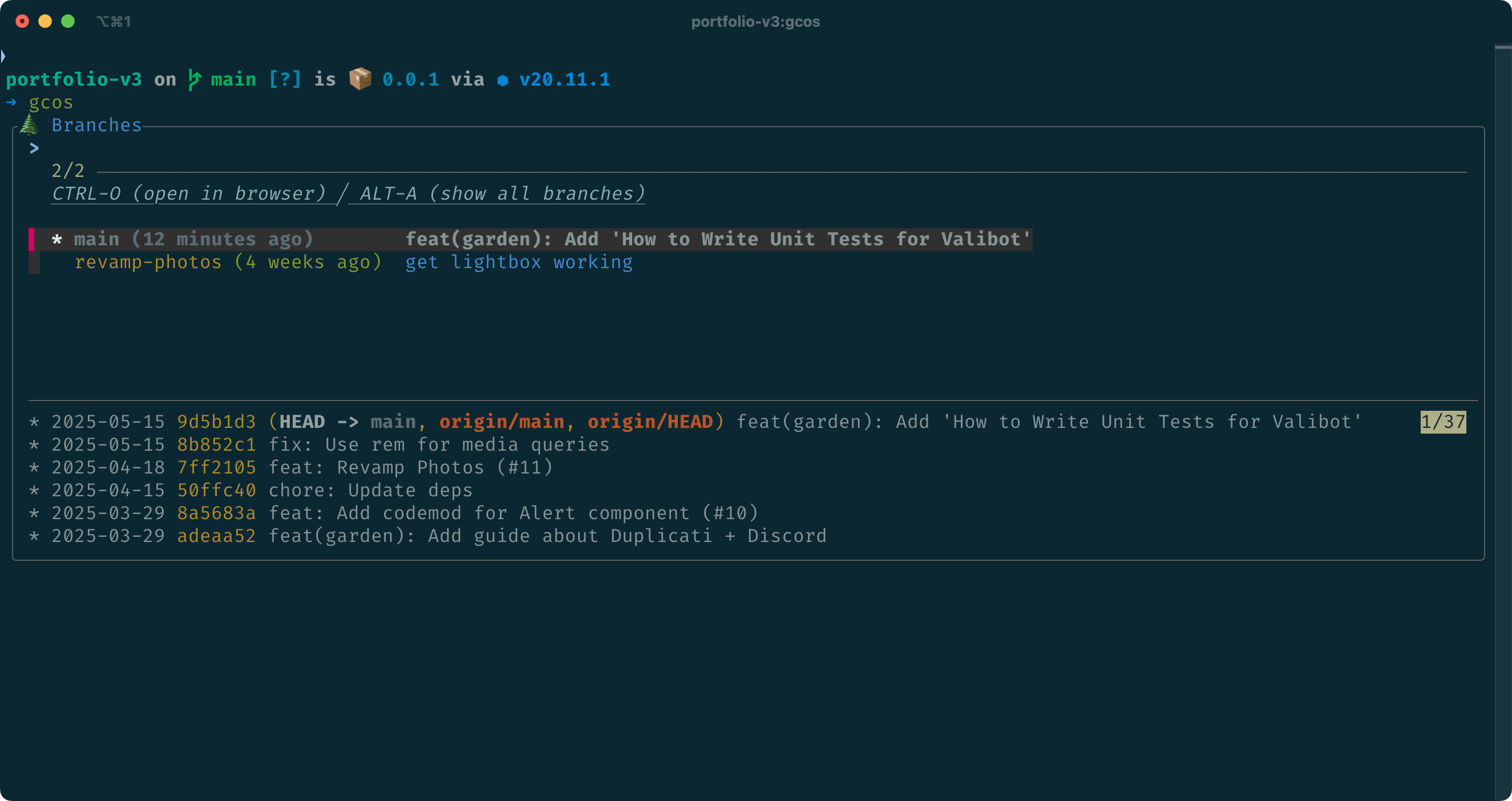
You can also use it to search through your files, tags, and more inside your CLI. The screenshot above shows a custom zsh function gcos() which uses fzf-git under the hood. You can also use fzf-git directly though.
-
Install fzf (opens in a new tab).
-
Install bat (opens in a new tab) for advanced syntax highlighting.
-
Locate your
.bashrcor.zshrcfile (typically in your$HOMEdirectory). Download thefzf-git.shfile from fzf-git (opens in a new tab) to this directory or a subdirectory. -
Source
fzf-git.shin your.bashrcor.zshrcfile:.zshrc source "$HOME/fzf-git.sh" -
Try out the keybindings defined in fzf-git usage section (opens in a new tab). For example, CTRL-G CTRL-B for branches.
To get the gcos() function shown in the screenshot, define a shortcut like so:
# Fuzzy-search branchesgcos() { _fzf_git_branches --no-multi | xargs git checkout}You can check the fzf-git.sh script for a list of all available functions.